Acta. Cryst. (2016) B72 661-683 (Feature Article) [ doi:10.1107/S2052520616012890 ]
 Direct determination of the Flack parameter as part of the structure refinement procedure usually gives different, though similar, values to post-refinement methods. The source of this discrepancy has been probed by analysing a range of data sets taken from the recent literature. Most significantly, it was observed that the directly refined Flack (x) parameter and its standard uncertainty are usually not much influenced by changes in the refinement weighting schemes, but if they are then there are probably problems with the data or model. Post-refinement analyses give Flack parameters strongly influenced by the choice of weights. Weights derived from those used in the main least squares lead to post-refinement estimates of the Flack parameters and their standard uncertainties very similar to those obtained by direct refinement. Weights derived from the variances of the observed structure amplitudes are more appropriate and often yield post-refinement Flack parameters similar to those from direct refinement, but always with lower standard uncertainties. Substantial disagreement between direct and post-refinement determinations are strongly indicative of problems with the data, which may be difficult to identify. Examples drawn from 28 structure determinations are provided showing a range of different underlying problems. It seems likely that post-refinement methods taking into account the slope of the normal probability plot are currently the most robust estimators of absolute structure and should be reported along with the directly refined values.
Direct determination of the Flack parameter as part of the structure refinement procedure usually gives different, though similar, values to post-refinement methods. The source of this discrepancy has been probed by analysing a range of data sets taken from the recent literature. Most significantly, it was observed that the directly refined Flack (x) parameter and its standard uncertainty are usually not much influenced by changes in the refinement weighting schemes, but if they are then there are probably problems with the data or model. Post-refinement analyses give Flack parameters strongly influenced by the choice of weights. Weights derived from those used in the main least squares lead to post-refinement estimates of the Flack parameters and their standard uncertainties very similar to those obtained by direct refinement. Weights derived from the variances of the observed structure amplitudes are more appropriate and often yield post-refinement Flack parameters similar to those from direct refinement, but always with lower standard uncertainties. Substantial disagreement between direct and post-refinement determinations are strongly indicative of problems with the data, which may be difficult to identify. Examples drawn from 28 structure determinations are provided showing a range of different underlying problems. It seems likely that post-refinement methods taking into account the slope of the normal probability plot are currently the most robust estimators of absolute structure and should be reported along with the directly refined values.
Publisher’s copy

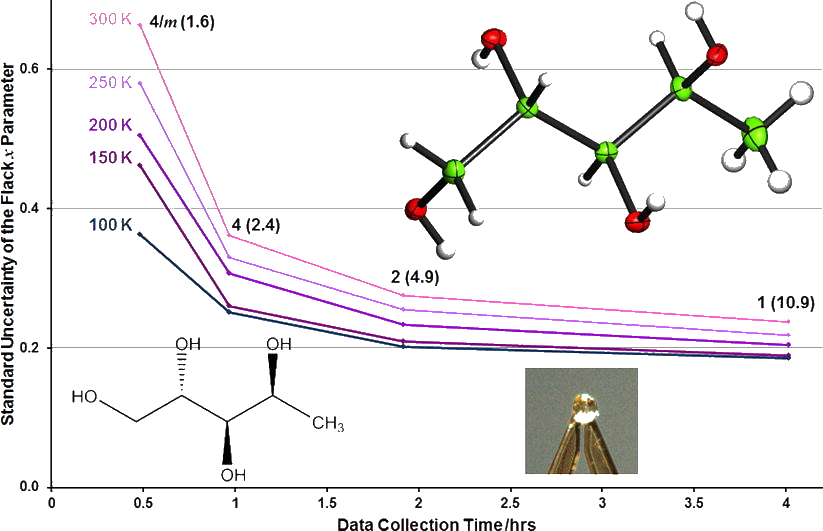
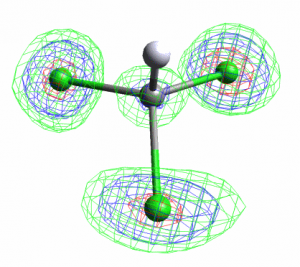

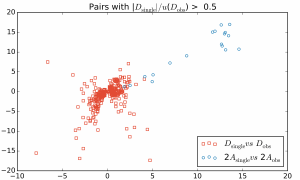
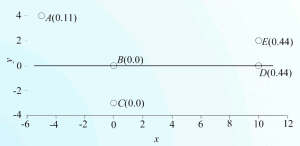 Leverages measure the influence that observations (intensity data and restraints) have on the fit obtained in crystal structure refinement. Further analysis enables the influence that observations have on specific parameters to be measured. The results of leverage analyses are discussed in the context of the amino acid alanine and an incomplete high-pressure data set of the complex bis(salicylaldoximato)copper(II). Leverage analysis can reveal situations where weak data are influential and allows an assessment of the influence of restraints. Analysis of the high-pressure refinement of the copper complex shows that the influence of the highest-leverage intensity observations increases when completeness is reduced, but low leverages stay low. The influence of restraints, notably those applying the Hirshfeld rigid-bond criterion, also increases dramatically. In alanine the precision of the Flack parameter is determined by medium-resolution data with moderate intensities. The results of a leverage analysis can be incorporated into a weighting scheme designed to optimize the precision of a selected parameter. This was applied to absolute structure refinement of light-atom crystal structures. The standard uncertainty of the Flack parameter could be reduced to around 0.1 even for a hydrocarbon.
Leverages measure the influence that observations (intensity data and restraints) have on the fit obtained in crystal structure refinement. Further analysis enables the influence that observations have on specific parameters to be measured. The results of leverage analyses are discussed in the context of the amino acid alanine and an incomplete high-pressure data set of the complex bis(salicylaldoximato)copper(II). Leverage analysis can reveal situations where weak data are influential and allows an assessment of the influence of restraints. Analysis of the high-pressure refinement of the copper complex shows that the influence of the highest-leverage intensity observations increases when completeness is reduced, but low leverages stay low. The influence of restraints, notably those applying the Hirshfeld rigid-bond criterion, also increases dramatically. In alanine the precision of the Flack parameter is determined by medium-resolution data with moderate intensities. The results of a leverage analysis can be incorporated into a weighting scheme designed to optimize the precision of a selected parameter. This was applied to absolute structure refinement of light-atom crystal structures. The standard uncertainty of the Flack parameter could be reduced to around 0.1 even for a hydrocarbon.